Why E-Commerce Growth Can Stay Stronger for Longer
An article “[Global E-Commerce Growth Forecast 2022](morganstanley.com/ideas/global-ecommerce-gr.. "morganstanley.com/ideas/global-ecommerce-gr..")” by Morgan Stanley says:
- In the initial days of COVID-19 e-commerce business surged and very soon it was picked up as all the shopping was done Online as retail locations were closed due to the virus spread.
- Overall retail sales in 2019 were 19% and it was picked up to 21% in the year 2021. It is roughly estimated that 22% of sales would be in 2022.
- It further states that even after COVID e-commerce market will grow in long term and could see a spike from $3.3 trillion today to $5.4 trillion in 2026.
- User purchase behaviour has changed over this period and it’s contributing to the growth and marketplace expansion.
E-commerce as a percentage of retail sales continues to grow across regions.
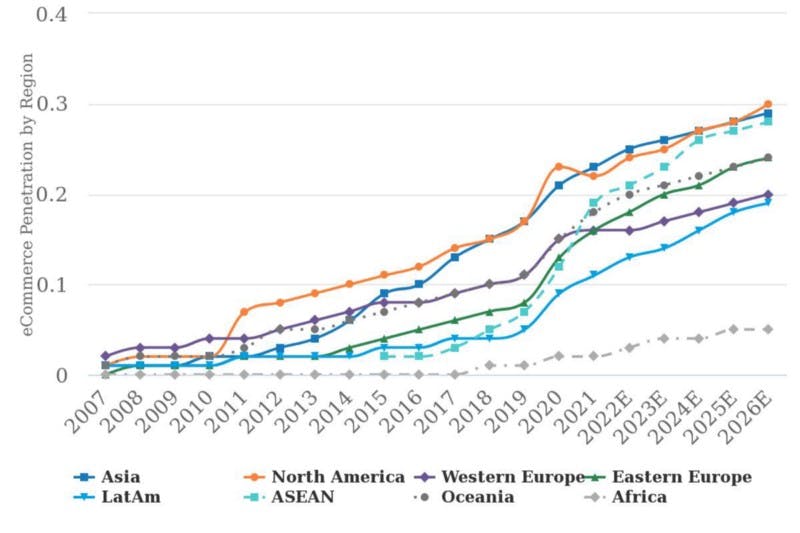
Source: Euromonitor, National Data Sources, Morgan Stanley Research estimates
What is Headless Commerce?
Now that we know how the e-Commerce market is going to grow over a period of time, it's time to discuss Headless Commerce.
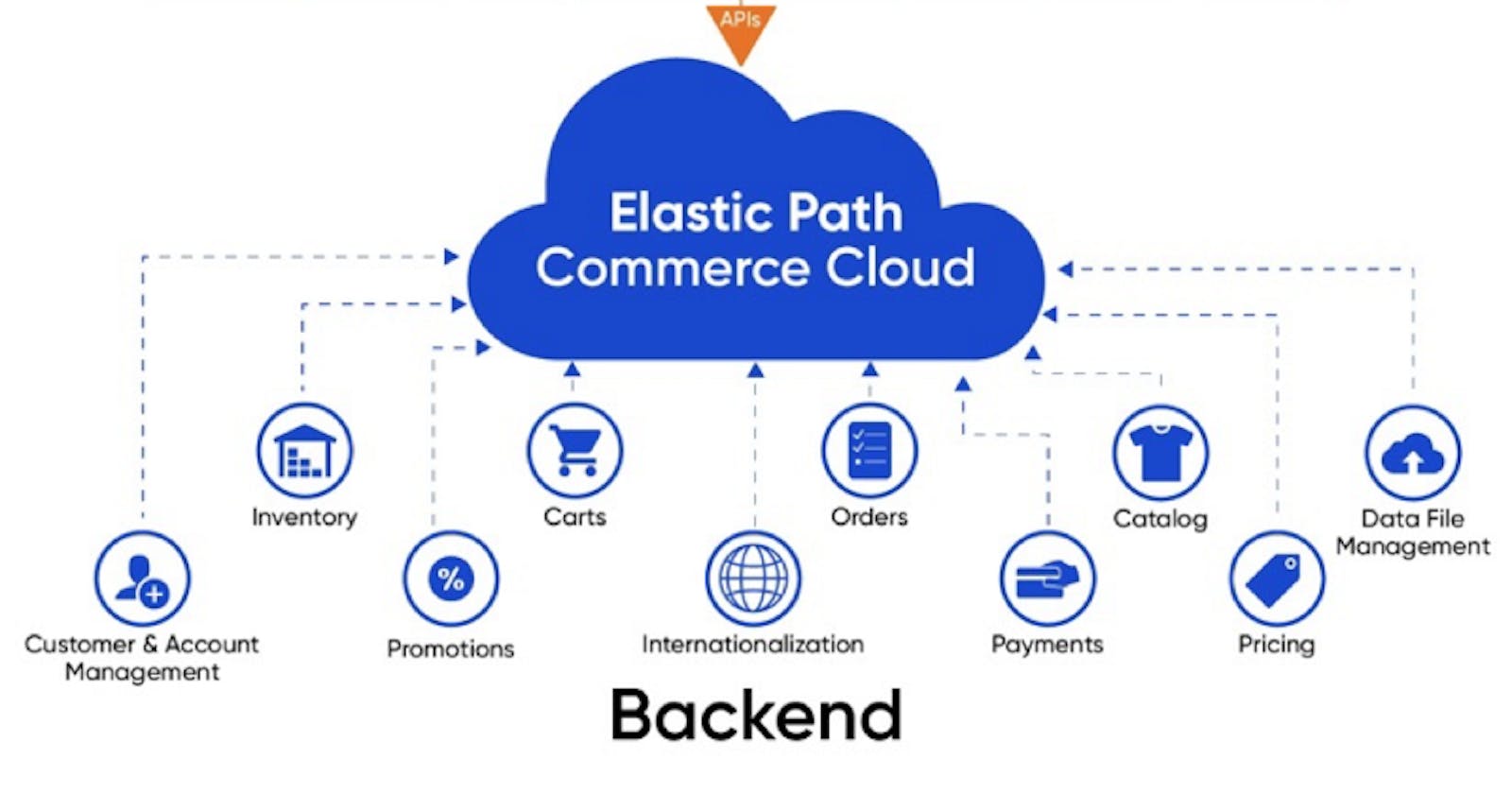
Headless commerce is an e-commerce architecture which decouples the front end from the backend. In other words, it decouples the customer-facing front-end application of eCommerce from the backend system's commerce functions and business logic.
Source: ElasticPath
What are the benefits of Headless Commerce?
- It is less error-prone since the front-end and back-end are decoupled.
- It will eventually help in causing less impact on each other and changes can be deployed smoothly.
- It helps in updating or editing front-end and back-end systems.
Coupled E-Commerce Vs Headless E-Commerce

Headless Commerce Providers
- [Adobe Commerce (formerly Magento Commerce)](business.adobe.com/products/magento/magento.. "business.adobe.com/products/magento/magento..")
- [Shopify Plus](shopify.com/plus/solutions/headless-commerce "shopify.com/plus/solutions/headless-commerce")
- [BigCommerce Enterprise](bigcommerce.com/solutions/headless-commerce "bigcommerce.com/solutions/headless-commerce")
- [CommerceTools](commercetools.com "commercetools.com")
- [Elastic Path](elasticpath.com/products/commerce "elasticpath.com/products/commerce")
- [Salesforce Commerce Cloud](salesforce.com/ap/products/commerce-cloud/o.. "salesforce.com/ap/products/commerce-cloud/o..")
- [SAP](sap.com/products/crm/e-commerce-platforms.h.. "sap.com/products/crm/e-commerce-platforms.h..")
- [OroCommerce Enterprise](oroinc.com/b2b-ecommerce/cloud "oroinc.com/b2b-ecommerce/cloud")
- [Spryker](spryker.com/headless-commerce "spryker.com/headless-commerce")
- [Swell](swell.is "swell.is")
- [SpreeCommerce](spreecommerce.org "spreecommerce.org")
- [Saleor](saleor.io "saleor.io")
Headless Commerce needs extensive levels of testing for a better customer experience
Headless Commerce communicate or interact with many systems at various level of technology and it requires extensive levels of testing which can cover all aspect.
Some of these layers include:
- Component Level Testing
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) Testing
- Integration Testing
- Database Testing
- User interfaces (UI) or presentation layer.
Typically testing can start from the Component level and APIs can be tested for each of these components. Reflect of data can be tested on UI, for example, if a payload value is changed how it reflects on the front-end if the content is changed from CMS then how it reflects on the front-end.
Covering all the aspects of the application can be challenging and requires an extensive amount of planning and execution to incorporate the rapid changes throughout the software life cycle.
What Do You Think?
Could I have done something better?
Have I missed something?
Please share your thoughts using comments on this post. Also, let me know if there are particular things that you would enjoy reading further.
Cheers!